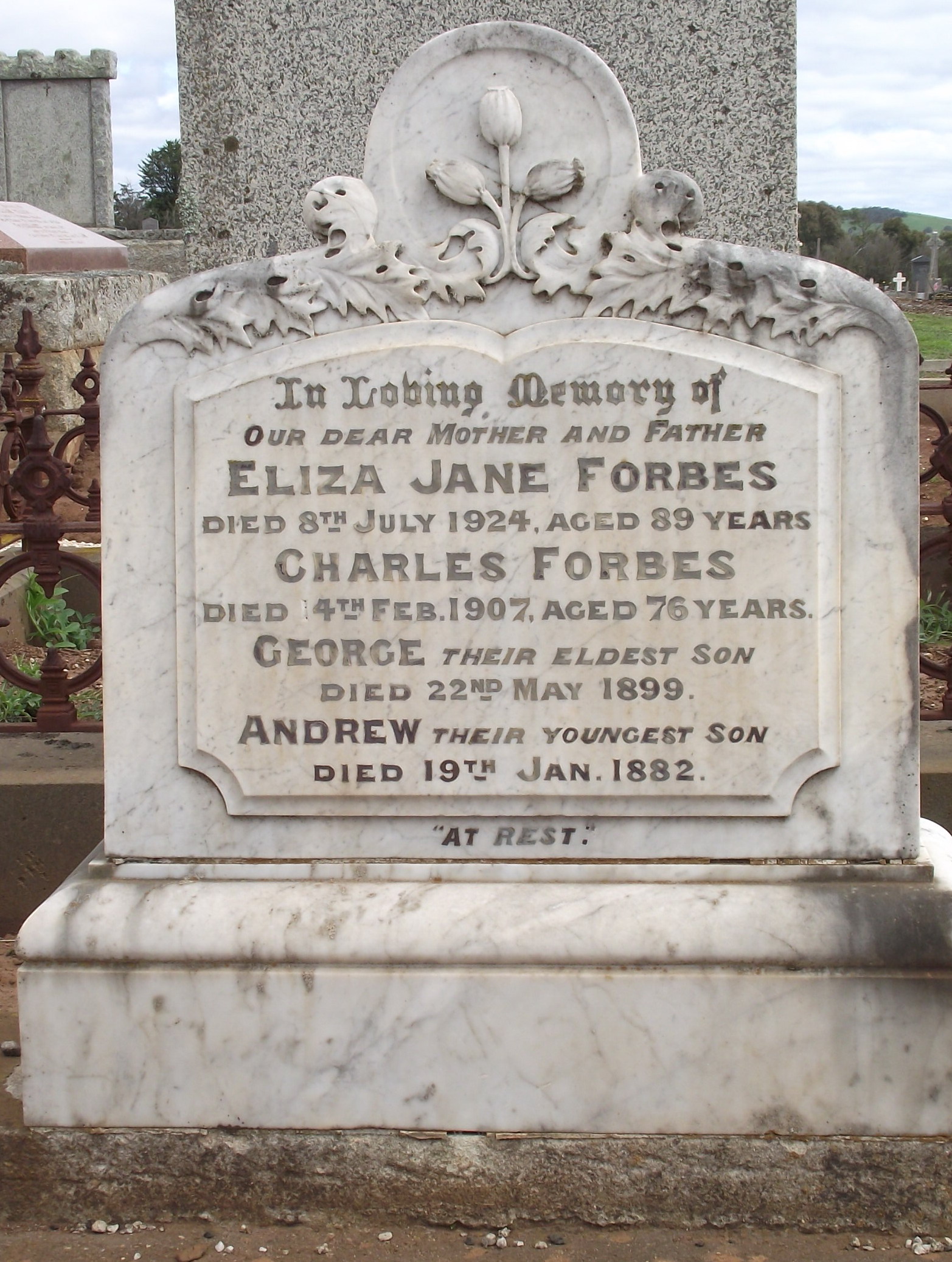Grave/Headstone
- types of stone used
HOW TO IDENTIFY MAJOR STONE TYPES
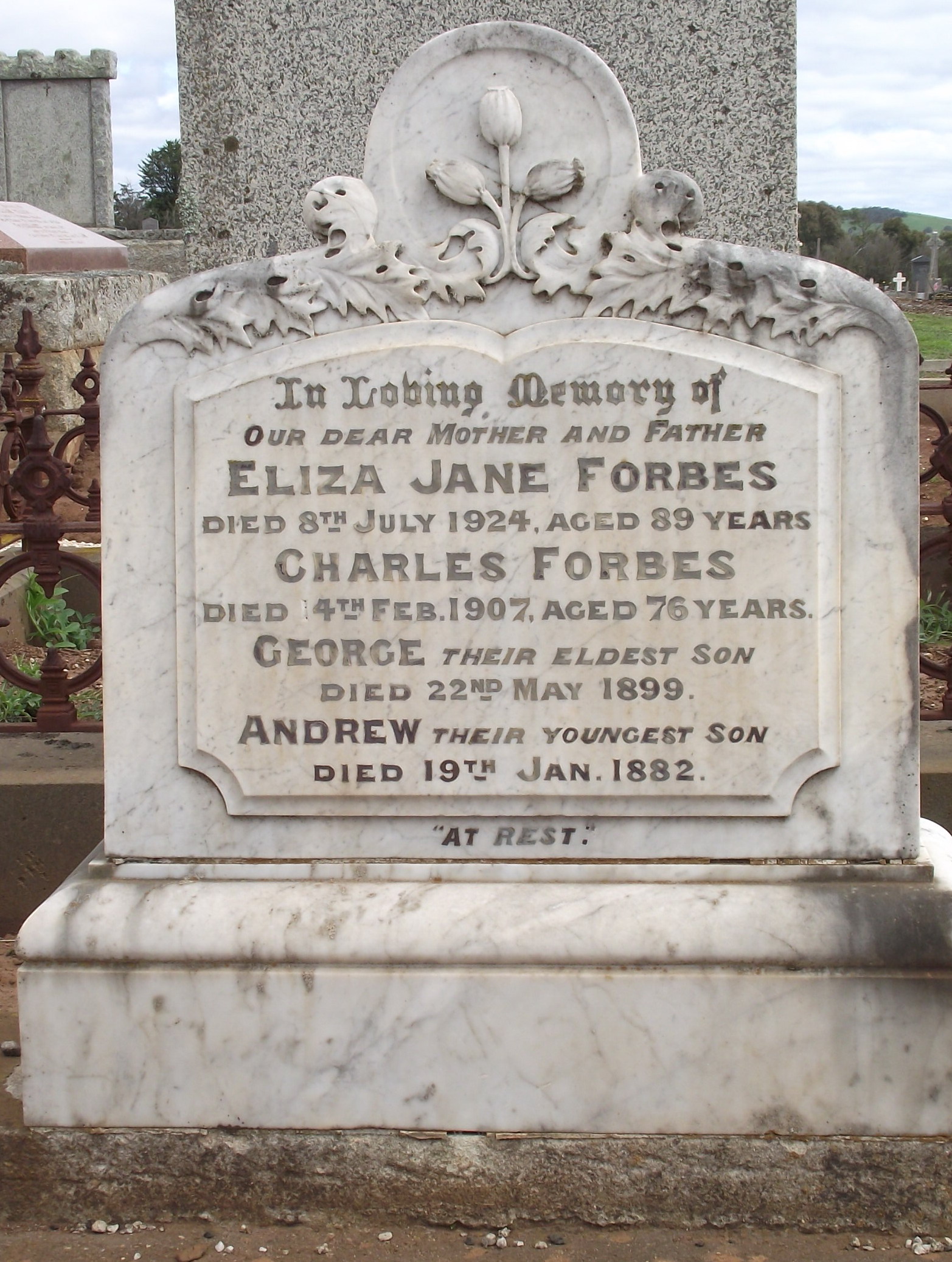
MARBLE
Hard, dense crystalline or granular metamorphic limestone
White when new or in new breaks, but older marbles may appear gray from soiling
Capable of taking a high polish, yellows with age
May have veins of gray or gold
Commercial marble is any lime carbonate capable of taking a polish, could include limestone and many
colors
Tennessee marble is medium-grained similar to limestone in texture with a pink cast
Georgia marble is very large-grained, somewhat gray in color
Predominant stone for gravestones in the 19th
century
Many early marbles are eroded and “sugaring”
SANDSTONE
Sedimentary rock composed of cemented sand grains – “bedding planes”
Red and brown (Brownstone) in color, can be gray, tan or blue (Bluestone)
Fine-grained stone with sand grains
Often flakes and delaminates

GRANITE
Igneous rock with visible grain, primarily quartz and feldspar
Speckled appearance with sparkly mica and dull black flecks
Extremely hard rock that is difficult to carve by hand
Grays, pinks in a wide range of colors
Commercial granites include gneiss and other rocks not strictly granite
Exhibits a full range of grain sizes with uniform surface patterns
Granular with no discernable bedding planes
Often used for monuments and tombs
SLATE
Metamorphosed shale, hard and brittle
Usually black, gray or blue
Sometimes fades with time
Extremely smooth, fine-grained stone with even bedding planes usually running parallel with the stone’s
face
Holds carving very well, inscriptions usually very clear
Uniform surface appearance
Gravestones tend to be thin and simple in shape, generally not more than six inches
LIMESTONE
Soft, sedimentary rock primarily composed of calcite
Fossils may be recognizable and are the most diagnostic trait
Tan, buff or gray colored that darkens with age
Matte surface almost never polished
Somewhat rough texture, rarely “sugars” like marble
No marked veining like marble
No definite layers or bedding planes like sandstone
No sparkly mica grains like granite
Often gets gypsum crusts
SOAPSTONE
Metamorphic rock
Largely composed of the mineral talc and is rich in
magnesium
Easily carved and darkens over age
Smooth to the touch
Used in 19th century,
commonly for slot and tab tombs in Georgia
White, gray, greenish gray, pale green, commonly discolored in reddish
or brownish hues and mottled
|